Skystorm's Post Production Supervisor, Warren Williams, and Senior Editor, Jason Chamberlain, unpacking the SAN. …
Commercial Production Crew Guide
Commercial Production Crew – Who Does What (Better Known as ‘What is a Best Boy’)
Producers
• Producer – The person in charge of the entire production from conception to completion and hand-off to the client. Depending on the size of the production, there may be several producers who are in charge of separate departments (finance, development, etc.) In commercial production you will usually see Executive and Line Producers.
• Executive Producer – The lead producer with complete oversight of a production. Usually works for a production company.
• Line-Producer – Primarily handles budgeting. May also oversee day to day operations on set including scheduling and equipment returns.
Director
• Director – Has control over all creative, including but not limited to deciding on content being shot, directing talent on set, final selections of set design and locations, managing lighting design and camera positioning. They are technically second in command to a producer (don’t say that to their face) but sometimes the roles are combined.
• 1st Assistant Director (1st AD) – On larger shoots a 1st AD is brought in as an assistant to the Director. They make sure that filming is on schedule, keep the crew organized and keep all production activity on track.
• 2nd Assistant Director (2nd AD) – They help supervise with the 1st AD and are in charge of making sure cast and crew have scripts, call sheets and other documents.
Camera
• Director of Photography (DP and/or Cinematographer) – This person is in charge of creating the ‘look’ of a project as captured through the camera. They recommend lighting, camera, and lensing and will work with the Director to design framing and camera movements.
• Camera Op – Controls the camera and framing during filming. This role can be performed by the Director of Photography in certain situations.
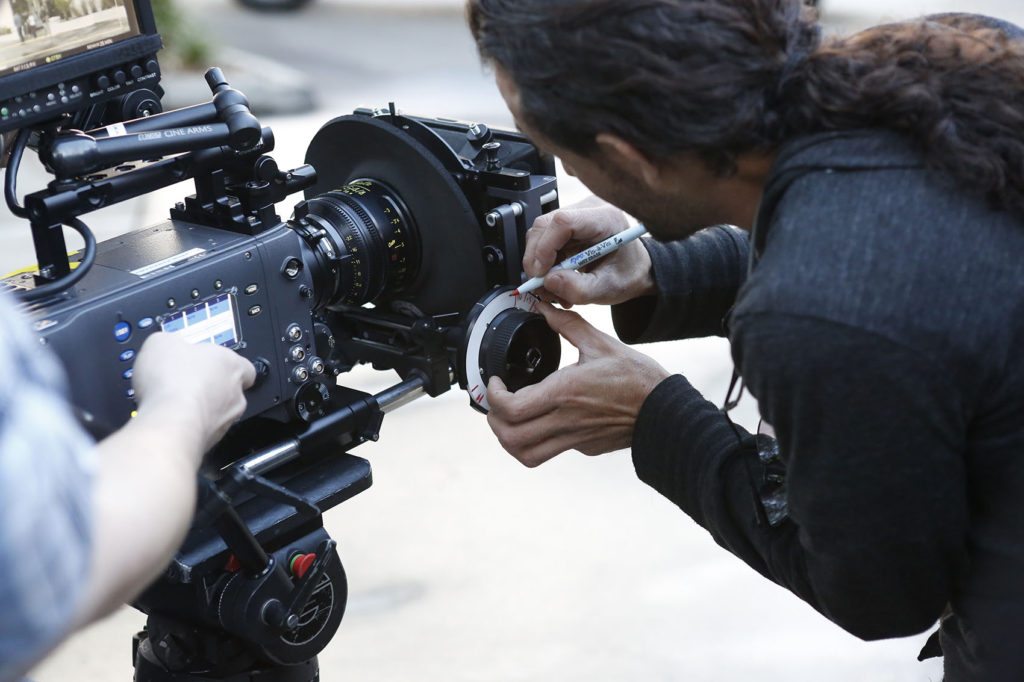
• 1st Assistant Camera (1st AC and/or Focus Puller) – They measure and maintain focus during filming and serve as main assistant to the Camera Op. They also build and dismantle the camera for filming and load filming media (SD cards, tape, etc.) as needed.
• 2nd Assistant Camera (2nd AC) – Generally, they will run the slate and take footage to the DIT. They also keep paths clear for Camera Op and 1st AC on moving camera shots.
• Digital Image Technician (DIT) – A stylized look such as black and white or high saturation levels are achieved in post – not through the camera during filming. The DIT is there to make sure that styling what is being filmed will actually be achievable during post production. They can also generate proxy files for Post to speed up the editing process and show footage to the DP for quality checks. During this process they also offload the footage and check that it’s safe and error free.
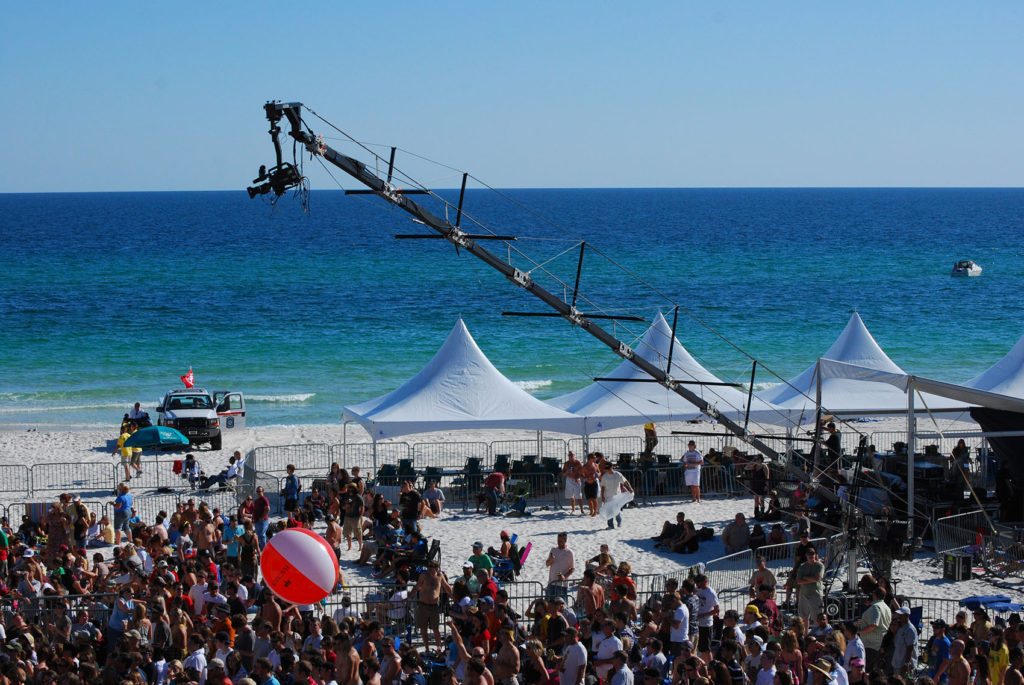
• Jib Op – Camera Op that controls jib arm for capturing elevated and large motion shots.
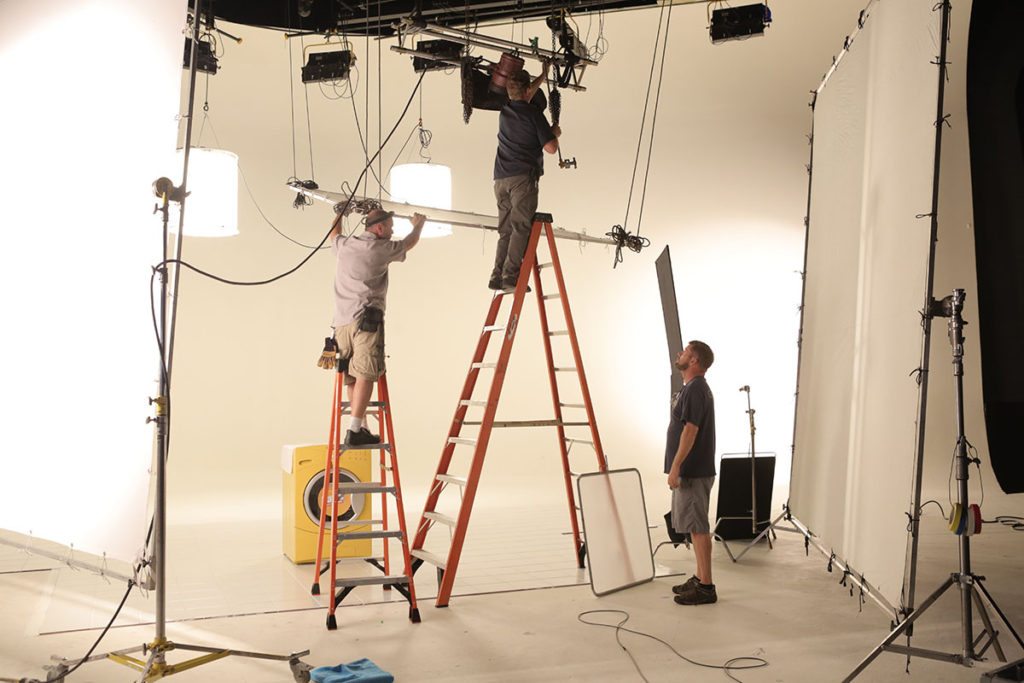
Lighting, Grip and Electric
• Gaffer – Head of lighting and grip, they design lighting for production based on instructions from the Director of Photography. The lighting plots are carried out by the Best Boy and Key Grip/Grips.
• Best Boy – Head of electrical and assistant to the Gaffer. Best Boy will use lighting plans from the gaffer to plan cabling and power needs for the production as well as tracking total electrical load on set.
• Key Grip – In charge of all grips. Works together with Best Boy, Gaffer, and DP to create lighting and power plans for production. Does not handle any electricity.
• Grips – Carries out non-electrical aspects of lighting. They are responsible for styling light as needed for the shot – using bounce boards, filters, gels, etc.
• Swing – Does both electrical and grip work as needed on set.
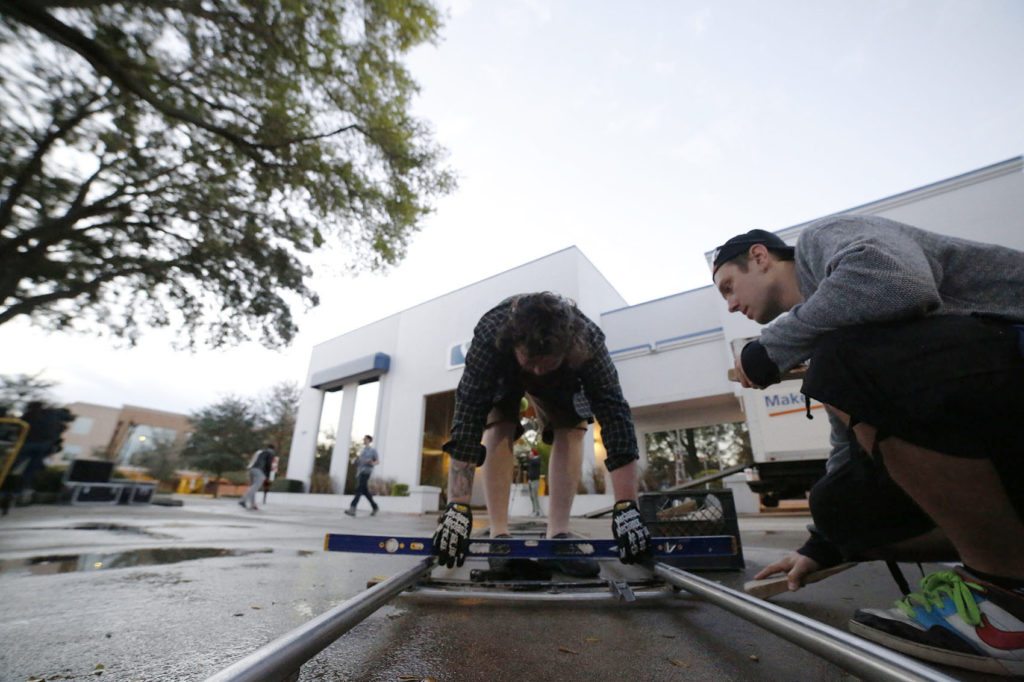

• Dolly Grip – Place, level, and move dolly track as well as push dolly with camera and Camera Op/1st AC while filming.
The biggest difference between all of these positions is the involvement of electricity. An overly simple way of explaining this would be that the Gaffer and DP come up with a lighting plot for the production. The Gaffer instructs the Best Boy and Key Grip on what needs to be done. The Best Boy runs power to the lights that are set up by the Key Grip and his team. The Key Grip and other grips on crew will then shape the light using tools such as flags and reflectors.
Art Department
• Art Director – Has oversight of the entire Art Department. This includes everything from props, costumes, set dressing and design. The end goal is to make sure the correct look and textures are achieved on camera.
• Prop-master – In charge of purchasing and maintaining anything that an actor touches or eats on camera. They also make sure that the items used are relevant to the time period being portrayed. On set, they monitor prop locations for continuity.
Sound
• Sound Mixer – Plan where and how microphones will be placed for production. They receive all audio from mics on set. They mix, level and monitor real time, and notify the Director of any audio interference during filming as well as keep audio logs to be used by the post department.
• Boom Operator – (Audio Assist and/or Utility) Holds and maneuvers the boom mic as well as mounting body mics. Since they are usually stationed very closely to talent, they can notify the Sound Mixer of any potential noise pollution coming from set that will need to be addressed.
Visual Effects
• VFX Supervisor – Logs camera data, set measurements and lighting diagrams to be used later in editing. They also monitor that what is filmed on set to make sure that it will be able to have visual effects properly applied in post. This may include laying marks on the object/person to be edited and making sure the speed of movement will be trackable in post. They work closely with the Camera Ops and ACs as they are involved in any camera and framing changes to make sure it doesn’t negatively impact the editing process.
Location
• Location Manager – Responsible for final securing of locations and location budgets for production. Reports to Production Manager or 1st AD.
• Location Scout – Does the research and visits potential shoot locations. Takes pictures and measurements as well as noting power sources or other production limitations.
Production Support
• Production Manager – Makes sure that the production stays on time and on budget on a day to day basis. They work very closely with the Production Coordinator and are generally working under the direction of the Line Producer.
• Production Coordinator – Coordinates the logistics of the production including renting equipment, hiring crew and talent, as well as handling paperwork such as release forms and nondisclosures.
• Production Assistant (PA) – This person is an assistant to all. They fill in any gaps and perform anything that requires additional hands from coffee runs to slate duties.
• Script Supervisor – If you have ever noticed an actor drinking from a glass where the amount in the glass keeps changing? A Scripty would have caught that. Their notes detail every shot and include things such as prop locations and scene blocking to ensure continuity both on set during filming and later in post-production. On set they will let the director know if there are any continuity errors that require a reshoot before striking the set. They keep track of what has been filmed, what needs to be filmed and what has been changed from the script. They also provide scene and take numbers for the sound mixer and slating.